
Pedestrian Protection- 行人保护仿真
- The Pedestrian Protection score is determined from tests to the most important vehicle front-end structures such as the bonnet and windshield, the bonnet leading edge and the bumper. In these tests, the potential risk at injuries to pedestrian head, pelvis, upper and lower leg are assessed.
Head impact
- Most pedestrian accidents occur within city areas where speeds are moderate. The head, the lower body and the legs are amongst the most frequently injured body regions. To estimate the potential risk of head injury in the event of a vehicle striking an adult or a child, a series of impact tests is carried out at 40 km/h using an adult or child head form impactor. Impact sites are then assessed and the protection offered is rated as good, adequate, marginal, weak or poor.The procedure promotes energy absorbing structures, deformation clearance and deployable protection systems such as pop-up bonnets and external airbags.
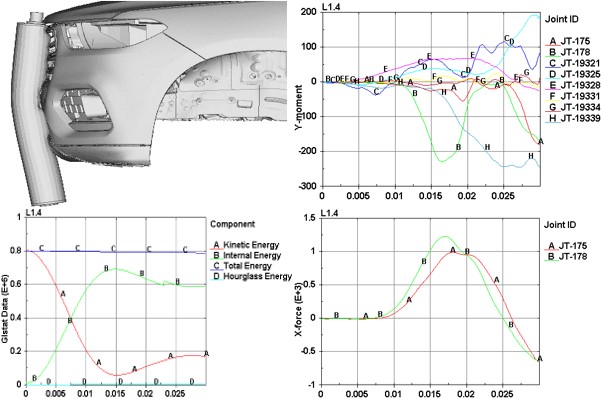
Upper Leg Impact
- To estimate the potential risk of pelvis and upper leg injuries in the event of a vehicle striking an adult, a series of impact tests is carried out at 40 km/h using an adult upper leg form impactor. Impact sites are then assessed and the protection offered is rated as good, adequate, marginal, weak or poor.The procedure promotes energy absorbing structures and a more forgiving geometry that mitigates injuries.
Lower Leg Impact
- To estimate the potential risk of leg injuries in the event of a vehicle striking an adult, a series of impact tests is carried out at 40 km/h using an adult leg form impactor. Impact sites are then assessed and the protection offered is rated as good, adequate, marginal, weak or poor. The procedure promotes energy absorbing structures and a more forgiving geometry that mitigates injuries to the leg.


你可能也喜欢 You May Also Like
多学科优化 Multidisciplinary Optimization
2023年1月31日
能源行业 Energy
2023年1月31日
