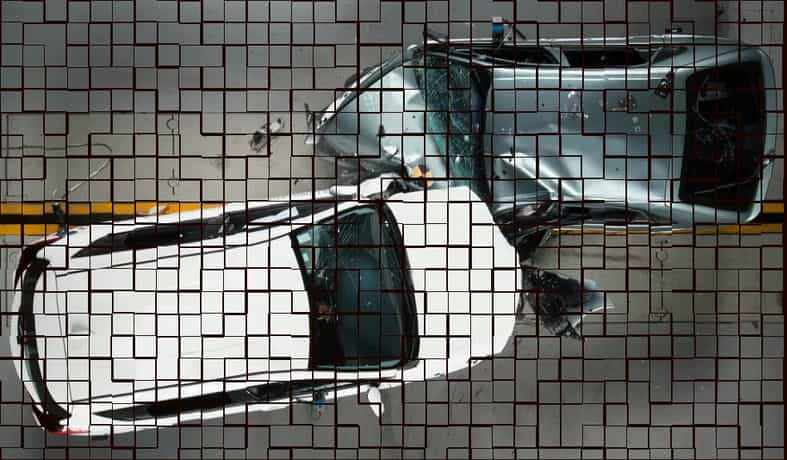
CAE仿真在汽车行业的应用
The phrase “design-build-test” has been used to accurately describe the tradition-al automotive development cycle. In recent years, however, the industry has set a new goal of 1-year from concept to reality. With such an aggressive target in mind, design-build-test approach has become increasingly impractical.
CAEFEA provides a solution to this problem with LS-DYNA, which can be used to replace a significant portion of physical testing with virtual testing. The bottom line is that firms can minimize rebuilding and retesting and ultimately save on de-velopment time and cost.

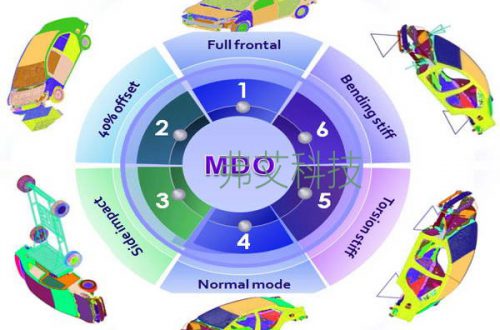
CAEFEA is already being used for a wide variety of automotive-related simulations. Some of the most common analysis types include:
• IIHS Offset Frontal Impact
• IIHS Side Impact
• IIHS Low Speed Bumper Impact
• FMVSS208 Frontal Impact
• FMVSS214 Static & Dynamic Side Impact
• FMVSS301 Rear Impact & Fuel Integrity
• FMVSS216 Roof Crush
• FMVSS225 Child Restraint Anchorage
• FMVSS201 Head Impact
• FMVSS207/210 Seatbelt Anchorage
• Gravity Loading
• Elastic Recovery After Dynamic Impact
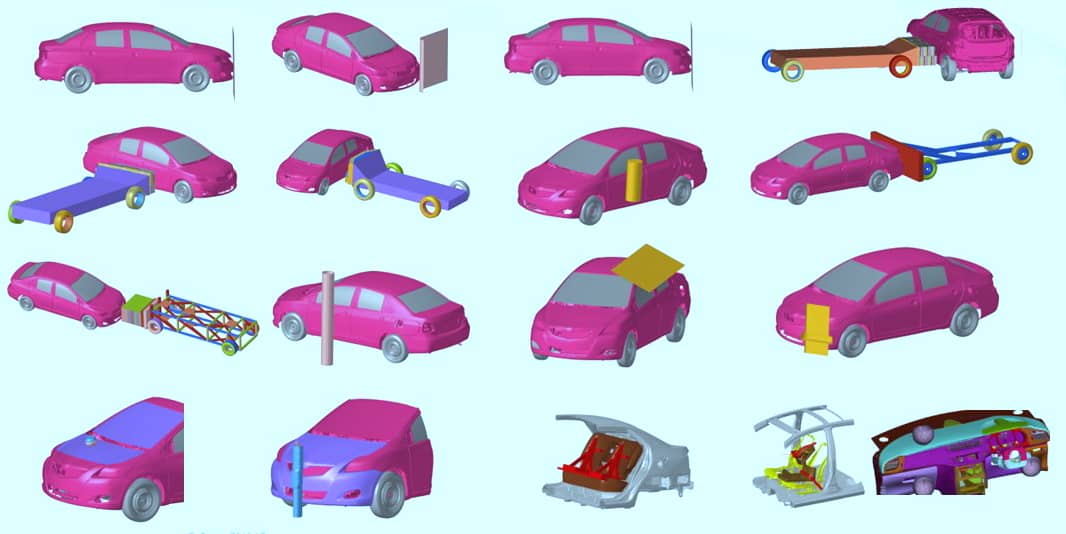
Such analyses encompass a wide variety of complex physical phenomena, and CAEFEA is equipped with vast array of features and capabilities to replicate these events. These include:
• An extensive library of materials (more than any other code) capable of ac-curately modeling steel, aluminum, plastics, fabric, glass, rubber, foam, honeycomb, and many others under both static and high-speed dynamic conditions. Many of these material models also capture viscous, rate-de-pendent, and hyperelastic behavior, and there is a wide variety of both brittle and ductile failure options available.
• An extensive selection of accurate and very general contact algorithms. These include surface-to-surface contacts, eroding contacts, tied interfaces, and many more.
• An extensive selection of airbag modeling tools. Available methods include Control Volume, ALE, and CPM.
• An extensive selection of seat belt related features, including sliprings, re-tractors, pre-tensioners, and sensors.
• An extensive selection of joining methods. These include rigid connections, bolts, and spotwelds. Delamination of boded structures can also be mod-eled.
• Multi-physics capabilities to model things like fluid-structure interaction in fuel tanks.


你可能也喜欢 You May Also Like
电子电器 Electronic
2023年1月31日
制造行业 Manufacture
2023年1月31日